PCIe FPGA Card
A10SA4
Arria 10 FPGA Low-Profile PCIe Card
QSFP28 and DDR4
Obsolete Product Notice:
This is an obsolete product and is no longer available for purchase. Contact BittWare for a recommended newer product.
Need a Price Quote?
Overview
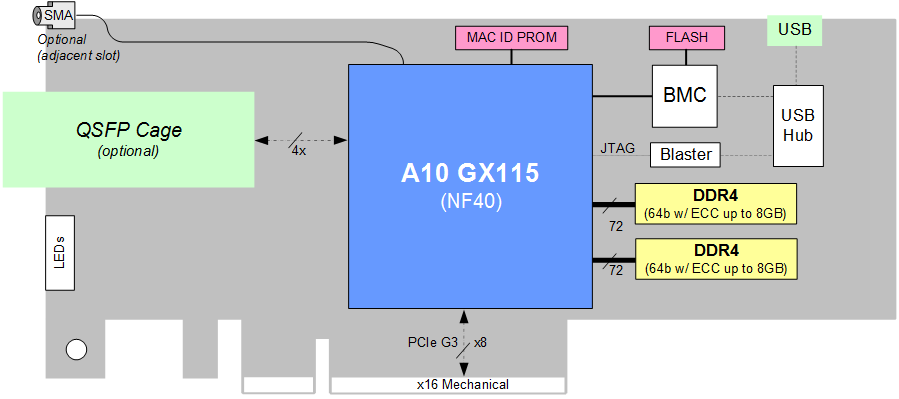
BittWare’s A10SA4 is a low-profile PCIe x8 card based on the Intel Arria 10 GX FPGA. Designed specifically to support large FPGA loads, the board offers an FPGA with up to 1150K logic elements, optional 10/40GbE high-speed networking, and up to 16GBytes DDR4 SDRAM – all of which make it ideal for server-based applications. OpenCL support enables a high-level software-like development flow, which greatly simplifies FPGA development.
The A10SA4 is designed with BittWare’s Spider platform, which is a low-profile PCIe platform optimized for thermal performance. The Spider platform combines a low-profile PCIe form-factor for high density, the ability to run larger loads, and a robust passive heatsink option designed for servers.
Key Features
Intel Arria 10 GX 1150
QSFP28 for 10/40 Gbps
OpenCL BSP
Video
Learn more about the A10SA4 card's key features.
Block Diagram, Data Sheet and Specifications
Want More Details?
Request the Hardware Reference Guide (HRG)
The HRG gives you much more detail about the card such as block diagrams, tables and descriptions.


Specifications
FPGA
- Intel Arria® 10 GX115 FPGA
- Up to 1150K logic elements available
- Up to 3,300 18x19 variable-precision multipliers
- High-performance, multi-gigabit transceivers @ up to 17 Gbps
On-Board Memory
- Two banks DDR4 with ECC, up to 8 GBytes (x72) each
- Flash with support for multiple boot images
- PROM for access to the board’s MAC ID
PCIe Interface
- x8 Gen1, Gen2, Gen3
- x16 mechanical interface
USB
- USB 2.0 interface for debug and programming FPGA and Flash
- Built-in Intel USB-Blaster
QSFP Cage
- Optional QSFP cage on front panel, supporting 40GbE or 4x 10GbE
- Can be optionally adapted for use as SFP+
Board Management Controller
- Voltage, current, temperature monitoring
- Power sequencing and reset
- Field upgrades
- FPGA configuration and control
- Clock configuration
- I2C bus access
- USB 2.0 and JTAG access
- Voltage overrides
Size
- Low profile (Half-height, half-length) PCIe slot card; x16 mechanical
- 168mm x 68.9mm
- Max. component height: 14.47mm
Development Tools
System Development
- BittWorks II Toolkit - host, command, and debug tools for BittWare hardware
FPGA HDL Development
-
- FPGA Development Kit - Example Quartus projects
- Intel tools - Quartus II software
OpenCL Development
-
- OpenCL Developer’s Bundle - BittWorks II Toolkit, Board Support Packages, Intel SDK for OpenCL, Intel Quartus II
Interested in Pricing or More Information?
Our technical sales team is ready to provide availability and configuration information, or answer your technical questions.
"*" indicates required fields